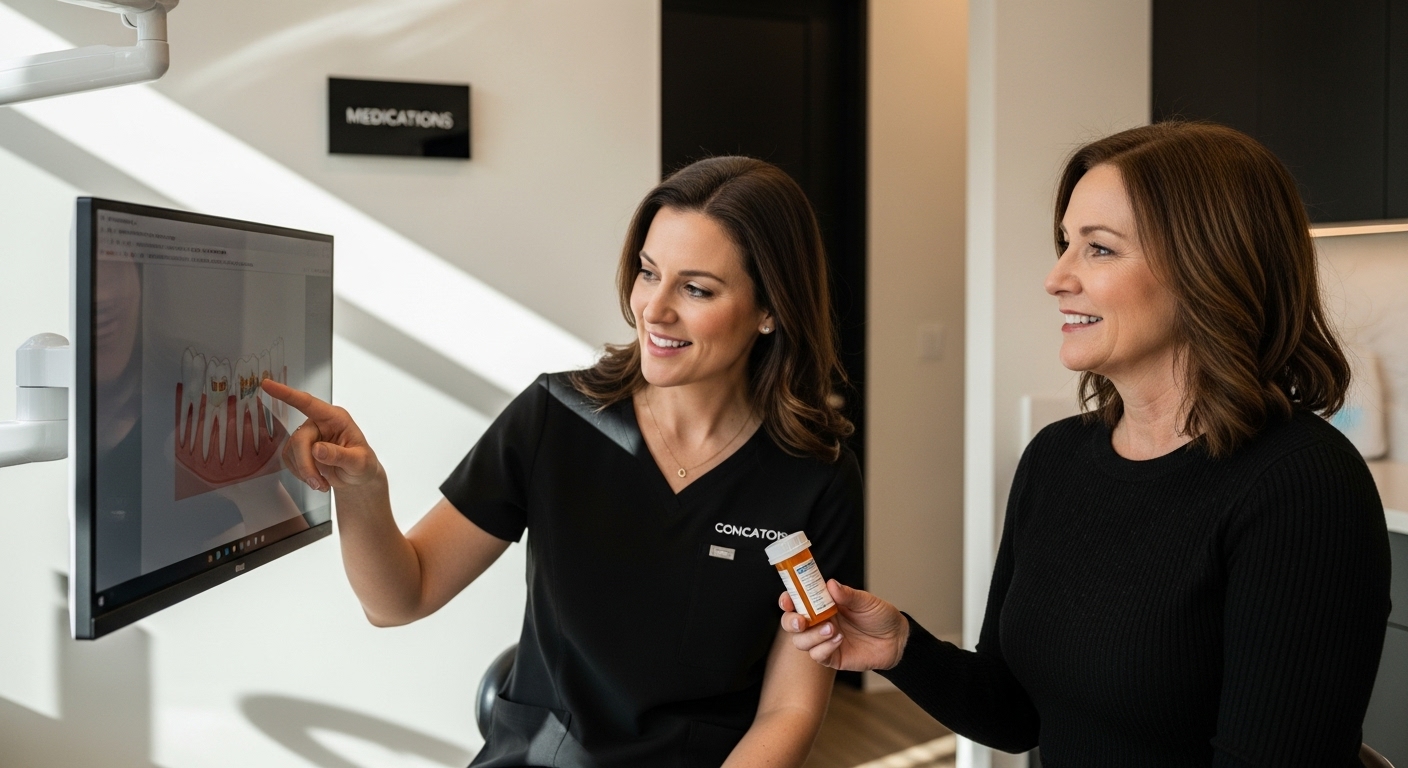
Medications can do wonders for your overall health, but they can also play unexpected tricks on your teeth. Over 400 common drugs are linked to dry mouth and increased cavity risk, a fact that surprises even seasoned patients. Most people never realize that the prescription in their medicine cabinet could quietly weaken their enamel or change the look of their smile.
Table of Contents
- What Are Medications That Affect Teeth?
- Why Do Certain Medications Impact Dental Health?
- How Medications Alter Tooth Structure And Function
- Common Medications And Their Effects On Teeth
- Managing Oral Health When Taking Medications
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Medications can cause dental problems. | Many medications affect oral health through side effects like dry mouth and gum inflammation. |
| Regular dental check-ups are crucial. | Routine visits help identify medication-related dental issues early, allowing for timely management. |
| Discuss medications with your dentist. | Sharing your full medication list helps dentists provide tailored advice for oral health protection. |
| Enhanced oral hygiene is essential. | Strong oral hygiene habits are necessary to combat potential side effects from medications that may damage teeth. |
| Stay informed about side effects. | Understanding how medications impact dental health empowers patients to adjust their care strategies proactively. |
What Are Medications That Affect Teeth?
Medications play a significant role in oral health, often impacting teeth in ways many patients do not anticipate. While prescription and over-the-counter drugs can provide essential health benefits, they can simultaneously create unexpected challenges for dental wellness. Understanding how medications that affect teeth function helps patients and healthcare providers make more informed decisions about treatment and preventive care.
Chemical Interactions and Oral Side Effects
Several medication categories can directly influence dental health through complex chemical interactions. Our guide on understanding tooth sensitivity provides additional context about how these interactions manifest.
According to research published in the National Institutes of Health, medications can impact teeth and oral health through multiple mechanisms:
- Reducing saliva production, which increases cavity and infection risks
- Causing chemical changes that alter tooth enamel structure
- Triggering inflammatory responses in gum tissues
- Creating opportunities for bacterial growth in the mouth
Common Medication Categories With Dental Implications
Certain medication groups are more likely to produce oral health side effects. Psychiatric medications like antidepressants frequently cause dry mouth, which can accelerate tooth decay. Blood pressure medications might cause gum inflammation, while some antibiotics can potentially stain developing teeth or impact tooth mineralization.
Antihistamines, painkillers, decongestants, and chemotherapy drugs also carry potential risks for dental health. Patients taking these medications should maintain regular dental check-ups and discuss potential oral health implications with their healthcare providers.
Beyond immediate effects, some medications can create long-term dental challenges that require proactive management and specialized dental care strategies.
The table below summarizes common categories of medications that impact dental health and the key oral side effects associated with each, helping readers quickly identify potential risks by drug type.
| Medication Category | Main Oral Side Effects | Sample Medications |
|---|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Dry mouth, higher cavity risk | SSRIs, Tricyclics |
| Blood Pressure Medications | Gum inflammation, overgrown gums | Calcium channel blockers |
| Antihistamines | Reduced saliva production | Loratadine, Diphenhydramine |
| Chemotherapy Drugs | Enamel erosion, tooth sensitivity | Methotrexate, Cisplatin |
| Antibiotics | Tooth discoloration (developing teeth) | Tetracycline |
| Immunosuppressants | Increased gum infection risk | Corticosteroids |
| Understanding these potential interactions empowers patients to protect their oral health while managing underlying medical conditions. |
Why Do Certain Medications Impact Dental Health?
Understanding the intricate relationship between medications and dental health requires examining the complex biochemical interactions occurring within the human body. Medications do not simply operate in isolation but interact with multiple physiological systems, creating cascading effects that can profoundly influence oral wellness. Learn more about protecting your oral health with our fluoride treatment guide.
Biochemical Mechanisms of Oral Interference
According to research published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, medications impact dental health through several sophisticated biochemical pathways:
- Altering saliva production and composition
- Modifying immune system responses
- Changing cellular metabolism in oral tissues
- Disrupting mineral absorption and integration
Saliva plays a critical protective role in maintaining oral health, acting as a natural defense mechanism against bacterial growth and tooth decay. When medications reduce saliva production or change its chemical composition, they create an environment more susceptible to dental problems.
Systemic Interactions and Oral Health Consequences
Different medication classes produce unique oral health challenges. Antihypertensive medications might trigger gum inflammation, while psychiatric drugs can cause dry mouth. Immunosuppressants can reduce the mouth’s natural defense mechanisms, increasing vulnerability to infections and periodontal diseases.
The body’s interconnected systems mean that medications targeting one health condition can inadvertently create secondary effects in oral tissues. Chemotherapy drugs, for instance, can compromise tooth enamel integrity and increase susceptibility to dental complications.
Patients taking multiple medications face compounded risks, with drug interactions potentially amplifying oral health challenges. Regular dental consultations and comprehensive medical history reviews become crucial in managing these complex interactions and developing personalized dental care strategies.
How Medications Alter Tooth Structure and Function
Medications can dramatically transform dental tissue composition and functionality through intricate biochemical processes that extend far beyond surface-level interactions. Understanding these complex mechanisms helps patients and dental professionals comprehend the profound impact pharmaceuticals can have on oral health. Explore how nutrition supports dental wellness in our comprehensive guide.
Cellular Level Transformations
According to research published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, medications interact with dental tissues through several critical pathways:
- Disrupting mineral absorption and integration
- Modifying cellular metabolism in dental tissues
- Altering protein synthesis in tooth-forming cells
- Interfering with calcium and phosphate metabolism
These interactions can fundamentally change how teeth develop, mineralize, and maintain structural integrity. Some medications can incorporate directly into developing tooth structures, creating permanent changes in color, strength, and composition.
Systemic Medication Effects on Dental Tissues
Certain medication categories produce distinctive impacts on tooth structure. Chemotherapeutic agents can cause direct toxicity to odontogenic cells, potentially impairing dentin and enamel formation. Antibiotics like tetracycline can cause intrinsic tooth discoloration by binding to calcium ions during tooth development, creating permanent structural modifications.
Bisphosphonate medications, typically used to treat bone disorders, can indirectly affect dental structures by altering bone metabolism. These drugs can reduce bone regeneration capacity, potentially compromising the supportive structures surrounding teeth and increasing risks of jaw-related complications.
The complexity of these interactions underscores the importance of comprehensive medical and dental histories. Patients taking medications that might influence dental health should maintain regular dental consultations to monitor potential structural changes and develop proactive prevention strategies.
Common Medications and Their Effects on Teeth
The complex interactions between pharmaceuticals and dental health reveal nuanced relationships that extend beyond surface-level understanding. Different medication categories can produce distinctive oral health impacts, transforming how patients approach both medical treatment and dental care. Explore how to maintain optimal oral health with our dental questions guide.
Medication Categories and Dental Risks
According to clinical research published in the Journal of Pharmacy Practice, multiple medication types create significant dental health implications:
- Antidepressants causing dry mouth and increased cavity risks
- Blood pressure medications triggering gum inflammation
- Antihistamines reducing saliva production
- Chemotherapy drugs compromising tooth enamel integrity
Each medication category interacts with oral tissues through unique biochemical mechanisms, potentially creating long-term dental challenges that require specialized preventive strategies.

Specific Medication Dental Side Effects
Psychiatric medications frequently produce pronounced oral health consequences. Antidepressants and antipsychotics often cause xerostomia, dramatically reducing saliva production and increasing bacterial growth potential. Calcium channel blockers can trigger gum overgrowth, while some antibiotics create permanent tooth discoloration by binding with developing dental tissues.
Immune system medications and treatments like corticosteroids can suppress natural oral defense mechanisms, increasing susceptibility to infections and periodontal diseases. Patients undergoing long-term pharmaceutical treatments must maintain rigorous oral hygiene and schedule frequent dental consultations to monitor potential structural changes and mitigate emerging risks.
Understanding these complex interactions empowers patients to work collaboratively with healthcare providers, developing comprehensive treatment approaches that protect both overall health and dental wellness.
Managing Oral Health When Taking Medications
Navigating oral health while managing pharmaceutical treatments requires strategic approaches that proactively address potential dental complications. Patients must develop comprehensive strategies to protect their teeth and gums from medication-induced challenges. Learn about maintaining excellent oral hygiene with our specialized guide.
Proactive Dental Protection Strategies
According to the American Dental Association, patients can implement several critical protective measures:
- Maintain frequent dental consultation schedules
- Practice enhanced oral hygiene routines
- Use specialized saliva replacement products
- Monitor medication side effects consistently
- Discuss potential dental risks with healthcare providers
Increasing water intake and utilizing sugar-free gum can help stimulate natural saliva production, which is crucial for maintaining oral microbiome balance and protecting tooth enamel.
Comprehensive Medication Management Techniques
Patients taking medications with potential dental side effects should develop a multifaceted approach to oral wellness. This involves collaborating closely with both medical and dental professionals to understand and mitigate potential risks. Specialized oral care products like neutral pH toothpastes, alcohol-free mouthwashes, and prescription-strength fluoride treatments can provide additional protection.
Regular dental screenings become especially important for individuals on long-term medication regimens. These appointments allow dentists to detect early signs of medication-related oral health changes, such as enamel erosion, gum inflammation, or increased cavity risks. Implementing personalized prevention strategies can significantly reduce the potential negative impacts of pharmaceutical treatments on dental health.
This table outlines protective strategies for managing oral health while taking medications, highlighting each strategy’s focus and potential benefits for patients concerned about medication-induced dental issues.
| Strategy | Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Regular dental check-ups | Early detection of dental changes | Identifies problems before they worsen |
| Enhanced oral hygiene | Preventing cavities and gum disease | Reduces plaque and bacteria buildup |
| Saliva replacement products | Alleviating dry mouth | Restores moisture, supports enamel |
| Increased water intake | Supporting natural saliva production | Helps wash away particles and acids |
| Sugar-free gum usage | Stimulating saliva flow | Balances oral microbiome, protects teeth |
| Neutral pH toothpaste & alcohol-free rinse | Reducing enamel erosion risk | Offers gentle, effective cleaning |

Don’t Let Medications Put Your Smile at Risk – Take Control of Your Oral Health Now
If you are worried about how your medications may be affecting your teeth, you are not alone. Many people face unexpected dental side effects such as dry mouth, gum inflammation, or changes in tooth strength after starting new prescriptions. When medications begin to disrupt saliva production or alter tooth enamel, the risk for serious oral health problems quickly rises. If you find yourself dealing with new dental discomfort or want to avoid permanent complications, proactive specialized care is essential.

Our team at Unity Square Dental understands the complex ways medications impact your oral health. We offer advanced, personalized solutions to help you protect your teeth and gums, with options like regular dental checkups and preventive treatments designed to counter medication side effects. Book your appointment today to consult with our caring professionals and create a prevention plan that supports your health and your smile. Visit https://unitysquaredental.ca now to take the first step toward long-term dental protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What medications commonly affect dental health?
Common medications that can impact dental health include antidepressants, blood pressure medications, antihistamines, chemotherapy drugs, and some antibiotics. These can cause side effects like dry mouth, gum inflammation, and potential tooth discoloration.
How do medications alter the structure of teeth?
Medications can disrupt mineral absorption and integration, modify cellular metabolism in dental tissues, and interfere with protein synthesis in tooth-forming cells. These changes can lead to issues like enamel erosion, tooth discoloration, and weakened dental structure.
What are the oral health risks associated with dry mouth caused by medications?
Dry mouth, often a side effect of medications, raises the risk of cavities, gum disease, and bacterial infections. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids and helping to wash away food particles, so reduced saliva increases dental problems.
How can I manage my oral health while taking medications?
To manage oral health while on medications, maintain regular dental check-ups, practice enhanced oral hygiene, use saliva replacement products, and discuss potential dental risks with your healthcare provider.