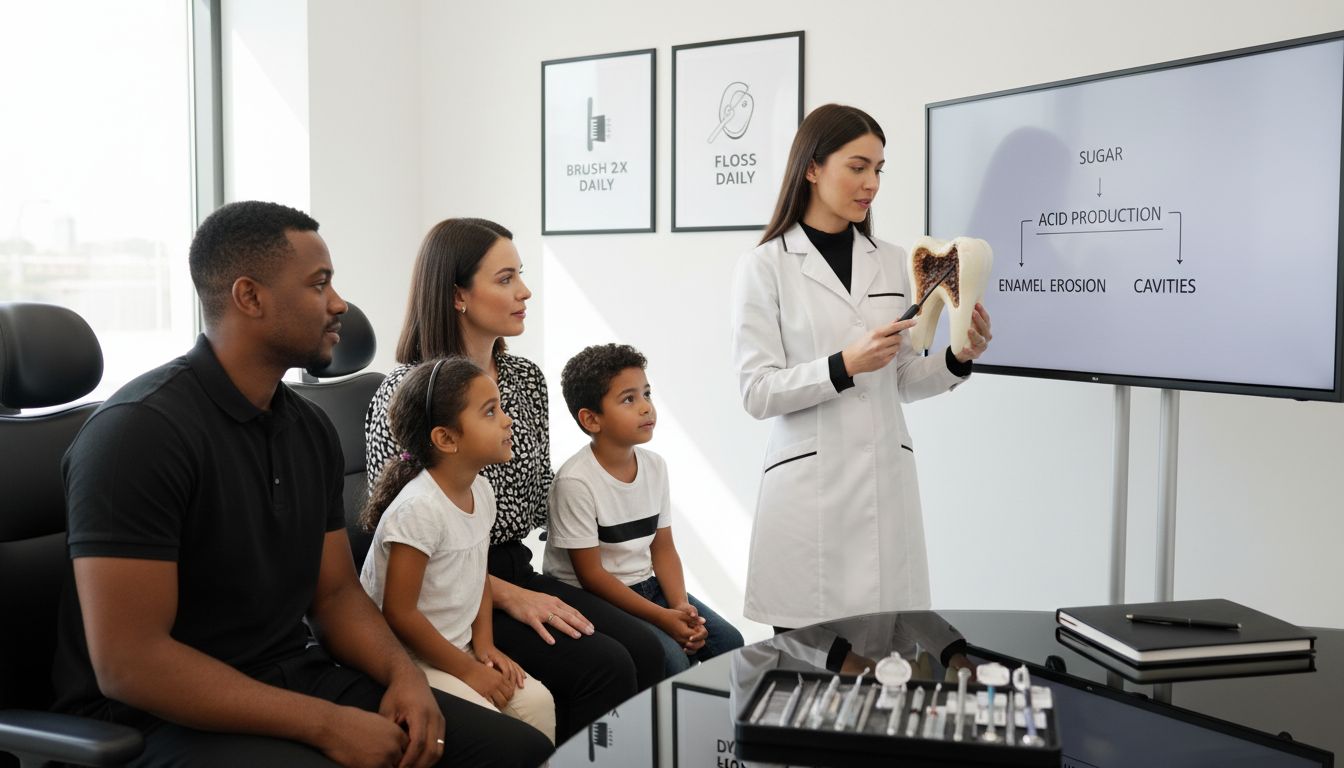
Every year, people worldwide spend billions treating dental issues that often start with a simple sweet tooth. Sugar doesn’t just lead to temporary toothaches. It fuels the very bacteria that cause decay, cavities, and gum disease. The science is clear—greater sugar intake means higher dental risk, and this reality affects both children and adults. This article reveals how sugar impacts oral health, why some types of sugar are more damaging than others, and what you can do to keep your teeth strong.
Table of Contents
- How Sugar Impacts Oral Health
- Types of Sugars and Their Dental Effects
- The Process of Tooth Decay and Cavities
- Risks: Cavities, Gum Disease, and Costs
- Preventing Sugar-Related Dental Damage
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar’s Impact on Oral Health | Increased sugar consumption leads to a higher risk of tooth decay and erosion due to acid production from bacteria. |
| Types of Sugars Matter | Not all sugars affect dental health equally; sucrose is particularly harmful due to its role in cavity formation. |
| Cavity Formation Process | Tooth decay begins quickly after sugar exposure, progressing through bacterial acid production and enamel damage. |
| Prevention Strategies | Effective dental care involves regular brushing, flossing, and limiting sugar intake to mitigate dental damage. |
How Sugar Impacts Oral Health
Sugar is more than just a sweet indulgence. It’s a direct threat to your dental health. According to a comprehensive study published in the Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology, there’s a significant positive correlation between sugar consumption and tooth decay, specifically measured through the decayed, missing, and filled teeth (DMFT) index.
When you consume sugary foods and drinks, a complex chemical process begins in your mouth. Harmful bacteria feed on these sugar particles, producing acid byproducts that attack tooth enamel. This acidic environment gradually erodes the protective layer of your teeth, creating microscopic holes and weakening your dental structure. A systematic review in the European Journal of Public Health further confirms this, revealing a dose-response relationship between sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and increased risk of dental caries and erosion.
The impact of sugar on oral health isn’t just about immediate damage. Repeated sugar exposure creates a cumulative effect that can lead to long-term dental problems. Here are key ways sugar undermines your dental health:
- Promotes bacterial growth in dental plaque
- Reduces tooth mineral content
- Increases risk of cavities
- Weakens tooth enamel
- Creates an acidic oral environment
To protect your teeth, it’s crucial to not just limit sugar intake but also practice excellent oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and understanding the connection between diet and dental health can help mitigate these risks and maintain a healthy smile.
Types of Sugars and Their Dental Effects
Not all sugars are created equal when it comes to dental health. According to research published in the Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology, sucrose stands out as particularly problematic for teeth. This type of sugar serves as a prime substrate for cariogenic bacteria, enabling them to produce acids that actively damage tooth enamel.
The complexity of sugar’s impact goes beyond simple consumption. A fascinating study in the Journal of Dental Research reveals that an individual’s unique oral microbiome can actually modify how different sugars interact with dental health. This means the same sugar might trigger different responses in different people, depending on their specific bacterial composition.
Here’s a breakdown of common sugar types and their potential dental risks:
- Sucrose (table sugar): Most harmful, rapidly metabolized by bacteria
- Fructose: Found in fruits, can contribute to acid production
- Glucose: Primary energy source for oral bacteria
- Lactose: Milk sugar, less damaging but still potential risk
- Artificial sweeteners: Generally considered less harmful to teeth
To protect your dental health, it’s crucial to understand these differences.
 Best foods for oral health can help you make informed dietary choices that minimize sugar’s negative impacts while maintaining a balanced diet.
Best foods for oral health can help you make informed dietary choices that minimize sugar’s negative impacts while maintaining a balanced diet.
The Process of Tooth Decay and Cavities
Tooth decay is a complex biological process that begins almost immediately after sugar comes into contact with oral bacteria. According to research from the Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology, this interaction triggers a destructive chain reaction. When sugar enters your mouth, oral bacteria rapidly metabolize it, producing acidic byproducts that start attacking tooth enamel within minutes.
The progression of tooth decay follows a predictable pattern. Initially, these acid attacks create microscopic demineralization zones on tooth surfaces. If left unchecked, these tiny vulnerabilities grow larger, eventually forming what dentists call dental caries or cavities. As highlighted by research from Allied Academies, repeated sugar exposure accelerates this destructive process, turning minor enamel weaknesses into significant dental health challenges.
Here’s a breakdown of the tooth decay progression:
- Sugar introduction
- Bacterial acid production
- Enamel demineralization
- Microscopic surface damage
- Cavity formation
- Potential tooth structure compromise
Preventing this process requires proactive dental care.
Causes of tooth decay guide can provide deeper insights into how you can interrupt this cycle and maintain optimal oral health.
Risks: Cavities, Gum Disease, and Costs
The consequences of sugar consumption extend far beyond a momentary sweet taste. According to research from NewMouth, excessive sugar intake creates a dose-response effect, where higher sugar consumption directly correlates with increased risks of dental problems and escalating treatment costs.
Beyond cavities, sugar’s impact reaches deeper into oral and systemic health. Research from the University at Buffalo reveals that high glycemic load foods can trigger complex health challenges, potentially linking poor oral health to broader medical complications. The financial burden is significant – repeated dental treatments, potential surgeries, and long-term interventions can transform a simple sugar habit into a substantial economic strain.
Key risks associated with high sugar consumption include:
![]()
- Rapid cavity development
- Accelerated tooth decay
- Increased gum disease risk
- Higher likelihood of periodontal complications
- Potential systemic health implications
- Substantial long-term dental treatment expenses
To mitigate these risks, understanding prevention becomes critical. How to prevent cavities naturally offers practical strategies to protect both your dental health and financial well-being.
Preventing Sugar-Related Dental Damage
Preventing sugar-related dental damage requires a strategic and proactive approach to oral health. According to research from Allied Academies, effective protection involves more than just occasional brushing. Comprehensive dental care means implementing a multi-layered strategy that addresses diet, hygiene, and lifestyle choices.
Nutrition plays a critical role in dental protection. NewMouth recommends strategic approaches to minimize sugar’s harmful effects. This includes not just reducing sugar intake, but also making smart substitutions and understanding how different foods interact with your oral microbiome.
Key prevention strategies include:
- Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss consistently to remove hidden food particles
- Choose tooth-friendly snack alternatives
- Limit frequency of sugar consumption
- Drink water after consuming sugary foods
- Regular dental check-ups
To support your dental health journey, 10 teeth friendly snacks can provide practical guidance on making smarter dietary choices that protect your smile.
Protect Your Smile From Sugar Damage Today
Sugar can quietly wear down your teeth and lead to painful cavities, gum disease, and costly dental treatments. The acid produced by bacteria feeding on sugar does more than create discomfort — it slowly erodes your enamel and weakens your smile’s strength. If you are looking to break this damaging cycle and maintain long-term dental health, understanding prevention and receiving personalized care are essential.

Discover how expert care at Unity Square Dental can help you combat sugar’s effects with advanced treatments and tailored advice. From routine cleanings to comprehensive dental services, our family-friendly clinic in Edmonton offers the support you need to protect your teeth daily. Don’t wait until small sugar-related damage turns into costly problems. Visit Unity Square Dental now and explore guidance on how to prevent cavities naturally and best foods for oral health. Take the first step toward a healthier, brighter smile today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does sugar contribute to tooth decay?
Sugar creates an acidic environment in the mouth when harmful bacteria metabolize it, leading to the erosion of tooth enamel and the formation of cavities.
What types of sugar are most harmful to dental health?
Sucrose, or table sugar, is particularly harmful because it is rapidly metabolized by bacteria. Other sugars like fructose and glucose can also contribute to tooth damage but to varying degrees.
What are the best practices for preventing sugar-related dental damage?
To prevent sugar-related dental damage, brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss regularly, limit sugar intake, and choose tooth-friendly snacks.
How does sugar impact oral health beyond cavities?
Excessive sugar intake can also increase the risk of gum disease, periodontal complications, and may lead to broader systemic health issues, along with escalating treatment costs for dental problems.