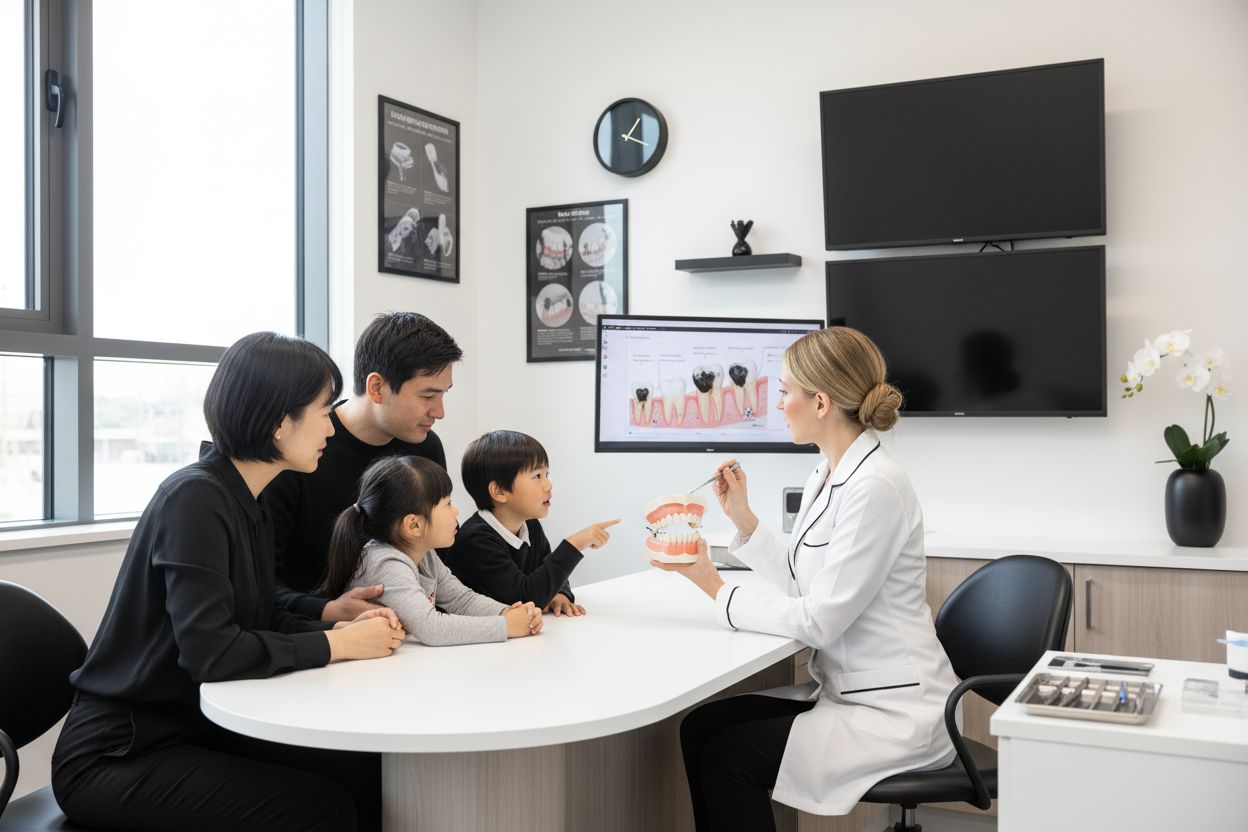
Did you know that nearly 100 percent of adults worldwide have experienced tooth decay at some point? Tooth decay is not just a minor inconvenience—it is a slow, complex disease that can lead to serious pain and even tooth loss if ignored. Many people mistakenly believe it only affects children or that cavities appear overnight. The truth is, understanding how tooth decay forms, what drives it, and how to prevent it can help you protect your smile for life.
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Tooth Decay as a Chronic Disease | Tooth decay is a complex disease influenced by bacteria on sugars, leading to gradual enamel breakdown. |
| Common Misconceptions | Misunderstandings include that only children get cavities or that all white spots are cavities; knowledge is key. |
| Prevention Strategies | Consistent oral hygiene and dietary choices, such as reducing sugar intake and using fluoride, are crucial for preventing decay. |
| Family Responsibilities | Dental health is influenced by family dynamics; collective responsibility can improve oral health outcomes for children. |
Table of Contents
- Tooth Decay Defined And Common Misconceptions
- How Cavities Form In Teeth
- Major Risk Factors For Tooth Decay
- Diet, Hygiene, And Bacterial Roles
- Preventing Tooth Decay In Everyday Life
Tooth Decay Defined and Common Misconceptions
Tooth decay isn’t just a simple cavity – it’s a complex chronic disease affecting billions worldwide. According to Wikipedia’s comprehensive research, dental caries represent a progressive breakdown of tooth structure caused by bacterial acids produced within dental plaque.
At its core, tooth decay occurs when harmful bacteria in your mouth transform sugars and carbohydrates into acid. This acid gradually erodes tooth enamel, creating tiny holes and weakening your dental structure. What most people don’t realize is that this process happens gradually – it’s not an overnight phenomenon but a long-term progression that can lead to serious complications like tooth loss, painful infections, and potential abscesses.
Common Misconceptions About Tooth Decay:
- Not all white spots on teeth are cavities
- Genetic predisposition doesn’t guarantee tooth decay
- Children aren’t the only ones susceptible to cavities
Here’s a comparison of common misconceptions vs. facts about tooth decay:
| Misconception | The Reality |
|---|---|
| All white spots are cavities | Many are enamel defects (e.g., chalky teeth) |
| Genetics guarantee cavities | Genetics influence risk but don’t determine outcome |
| Only children get cavities | All ages are susceptible |
| Tooth decay happens overnight | Decay is a gradual, long-term process |
One fascinating insight relates to what experts call “chalky teeth” – a condition often mistaken for standard tooth decay. According to research, these opaque, porous areas actually stem from developmental enamel defects like hypomineralisation, fluorosis, or genetic conditions. These areas might look concerning, but they aren’t automatically cavities.
The key takeaway? Understanding tooth decay means recognizing it as a complex, preventable condition that requires consistent oral hygiene and professional dental care. Knowledge truly is the first step toward maintaining a healthy smile.
How Cavities Form in Teeth
Cavity formation is not a random event but a precise biological process involving multiple interconnected elements. According to Wikipedia’s dental research, four critical components must converge to create a cavity: a susceptible tooth surface, specific bacteria, fermentable carbohydrates, and sufficient time.
The process begins with dental plaque – a sticky biofilm harboring bacterial colonies that thrive on sugars. When you consume foods containing carbohydrates, these bacteria metabolize the sugars and produce acid as a byproduct. This acidic environment starts attacking your tooth’s protective enamel, creating microscopic demineralization zones that gradually expand if left unchecked.
The Cavity Formation Stages:
- Initial bacterial colonization
- Acid production from sugar metabolism
- Enamel demineralization
- Structural breakdown of tooth surface
- Cavity development
A fascinating mathematical model recently published reveals that cavity progression isn’t linear but a complex reaction-diffusion process. This research suggests that enamel demineralization occurs through intricate chemical interactions, with acid exposure creating anisotropic effects that determine how quickly and in what patterns tooth structure breaks down.
Prevention remains the most effective strategy.
VIDEO:video_content] By understanding these mechanisms, you can interrupt the cavity formation cycle through regular oral hygiene, balanced nutrition, and [professional dental care that helps protect and remineralize tooth surfaces.
Major Risk Factors for Tooth Decay
Tooth decay risks are far more complex than most people realize. According to research from Quebec’s health resources, multiple interconnected factors contribute to dental deterioration, ranging from personal habits to genetic predispositions.
Oral hygiene stands as the primary defense against decay. Poor dental practices dramatically increase cavity risks, including infrequent brushing, neglecting fluoride treatments, and inconsistent cleaning routines. Diet plays an equally critical role – frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth. Interestingly, habits like sleeping with sugary drinks or constant snacking accelerate tooth damage by providing continuous fuel for harmful bacteria.
Key Tooth Decay Risk Factors:
- Inadequate oral hygiene
- High sugar diet
- Frequent snacking
- Dry mouth conditions
- Inherited bacterial transmission
- Medication side effects
Family dynamics also significantly impact dental health. Groundbreaking research from BMC Oral Health reveals that parental factors like exhaustion, relationship challenges, and untreated dental issues strongly correlate with higher cavity prevalence in children. This suggests that dental health is not just an individual concern but a family-wide responsibility.
Managing these risks requires a holistic approach.
 Learn more about protecting your family’s dental health through professional guidance, understanding medication impacts, and developing comprehensive oral care strategies.
Learn more about protecting your family’s dental health through professional guidance, understanding medication impacts, and developing comprehensive oral care strategies.
Diet, Hygiene, and Bacterial Roles
The battle against tooth decay is fundamentally a microscopic war waged in your mouth. Research from BMC Public Health reveals that diet plays a nuanced role – not just as a potential threat, but also as a potential defender of dental health.
Dietary Impacts are complex and multifaceted. While sugary and sticky foods accelerate decay by providing rapid fuel for harmful bacteria, certain foods actually help protect teeth. Complex carbohydrates, dairy products, and fiber-rich foods stimulate saliva production, which naturally neutralizes harmful acids and helps remineralize tooth enamel. Think of saliva as your mouth’s built-in defense mechanism.
Key Bacterial Management Strategies:
- Reduce sugary food intake
- Increase saliva-stimulating foods
- Practice consistent oral hygiene
- Use targeted cleaning techniques
- Monitor bacterial population
According to specialized microbiology research, managing oral microbiota is crucial. Streptococci and Lactobacilli bacteria are primary culprits in tooth decay, and their population can be significantly reduced through strategic dietary choices and rigorous oral hygiene. Enamel erosion creates additional challenges by facilitating biofilm buildup, making prevention even more critical.
Understanding these intricate relationships empowers you to make informed choices. Read our comprehensive guide on teeth-friendly nutrition to learn how to transform your diet into a powerful ally in dental health.
Preventing Tooth Decay in Everyday Life
Tooth decay prevention isn’t about complicated medical interventions, but consistent daily habits. According to comprehensive research from Very Well Health, protecting your dental health involves straightforward strategies you can implement immediately in your daily routine.
Your oral hygiene arsenal should include fundamental techniques like brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, meticulous flossing, and maintaining regular dental check-ups. Dietary choices play an equally critical role. Limiting sugary and starchy foods, staying hydrated to promote saliva production, and being mindful of snacking habits can significantly reduce cavity risks. Surprisingly, simple actions like quitting smoking and regularly replacing your toothbrush can make substantial differences in long-term dental health.
Daily Prevention Strategies:
- Brush teeth twice daily
- Use fluoride toothpaste
- Floss regularly
- Limit sugar intake
- Stay hydrated
- Replace toothbrush every 3-4 months
- Schedule routine dental check-ups
Wikipedia’s dental research highlights additional preventive measures like applying dental sealants on molars and systematically reducing free sugar consumption. These approaches have demonstrably reduced tooth decay prevalence in developed regions. The key is consistency – small, repeated actions create significant long-term protection.

Discover more about maintaining optimal oral health through strategic nutrition and lifestyle choices that support your dental wellness journey.
Take Control of Tooth Decay for Your Whole Family
Are you worried about the hidden and complex threat of tooth decay described in this guide? Daily habits, family routines, and even small nutrition choices all play a part in keeping your family safe from cavities and dental pain. At Unity Square Dental, we understand the emotional stress parents feel when trying to protect their children’s smiles, especially when so many factors—like genetics, diet, and bacteria—can make it seem impossible to stay ahead.

Your family deserves care built around understanding, comfort, and real expertise. That is why Unity Square Dental is here, right in Edmonton, offering advanced technology and a personalized approach for every patient. Ready for practical guidance, tailored prevention plans, and a team who truly listens? Visit our dental clinic page to book your visit or explore our oral health guides for immediate tips you can use. Protect what matters most—schedule your appointment today for a lifetime of healthy, confident smiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of tooth decay?
Tooth decay is primarily caused by harmful bacteria in the mouth that produce acid when they metabolize sugars and carbohydrates. This acid erodes tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
How can I tell if I have tooth decay?
Signs of tooth decay include tooth sensitivity, visible holes or pits in your teeth, white spots on the enamel, and pain when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet foods.
What are effective strategies for preventing tooth decay?
To prevent tooth decay, maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine by brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing regularly, limiting sugar intake, and scheduling routine dental check-ups.
Does diet impact tooth decay?
Yes, diet plays a crucial role in tooth decay. Foods high in sugar and acids can promote bacterial growth, while dairy products and fiber-rich foods can help protect teeth by stimulating saliva production and neutralizing acids.