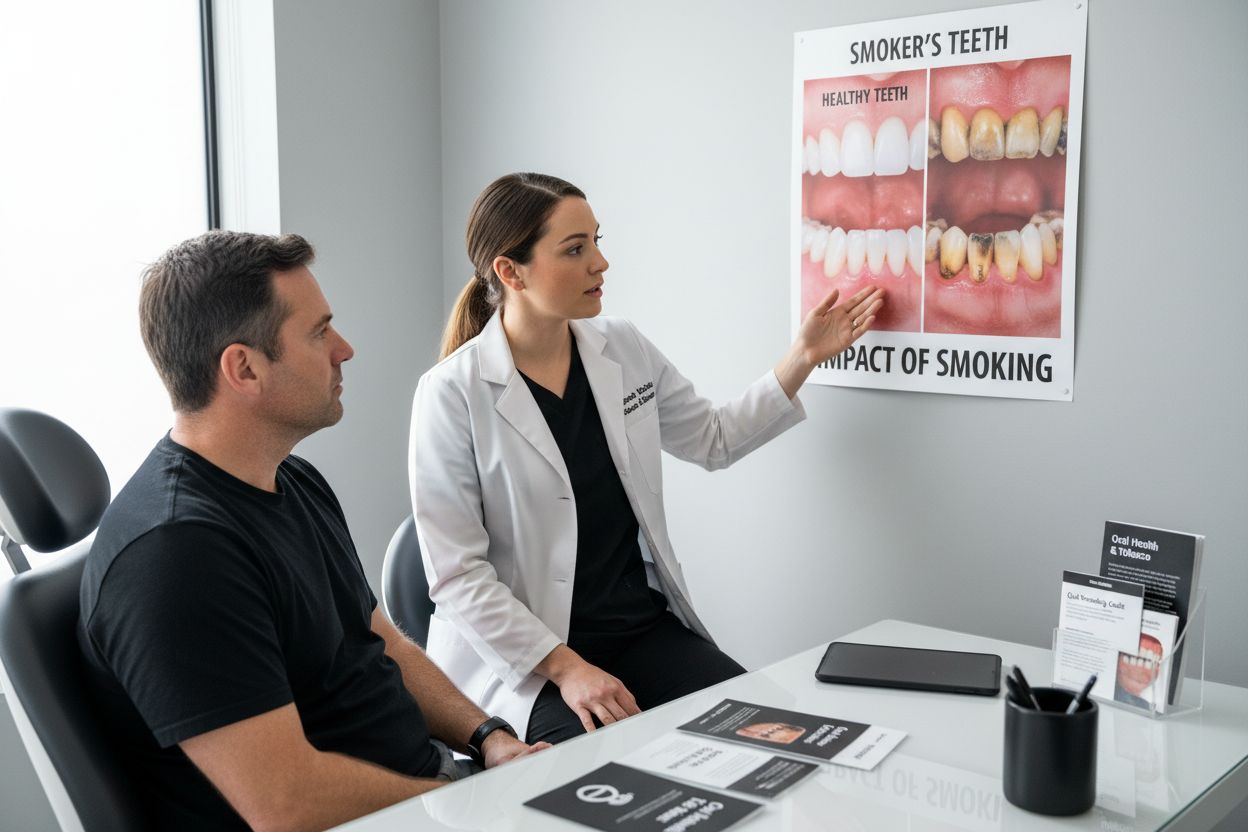
Smoking does more than leave a lingering smell or yellow teeth. The real shock is how it can quietly destroy the entire foundation of your oral health over time. In fact, smokers face up to double the risk of gum disease compared to non-smokers, and yet most people never realize just how deeply every drag affects their gums, teeth, and even future cancer risk until it’s too late.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Relationship Between Smoking And Oral Health?
- Why Does Smoking Significantly Affect Dental Health?
- How Does Smoking Contribute To Oral Diseases?
- What Are The Long-Term Effects Of Smoking On Teeth And Gums?
- What Steps Can Be Taken To Mitigate Smoking’s Impact On Oral Health?
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Smoking worsens oral health significantly | Tobacco disrupts vital biological processes, harming dental integrity and soft tissues. |
| Chronic smoking leads to severe gum disease | Long-term tobacco use increases the risk of periodontitis and other serious infections. |
| Smoking alters oral microbiome negatively | Hazardous compounds from smoking encourage harmful bacteria, reducing beneficial ones and increasing decay risk. |
| Professional dental care is essential | Regular dental visits allow early detection and targeted treatments to counteract tobacco damage. |
| Quitting smoking promotes healing | Stopping tobacco use enables natural recovery of damaged oral tissues and improves overall health. |
What is the relationship between smoking and oral health?
Smoking profoundly disrupts oral health through multiple complex mechanisms that gradually compromise dental and soft tissue integrity. Research from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirms that smoking dramatically increases risks of serious oral health complications.
Chemical Warfare Against Oral Tissues
When you smoke, tobacco introduces a toxic chemical cocktail directly into your mouth. Nicotine, carbon monoxide, and hundreds of additional harmful compounds interact destructively with oral tissues. These chemicals immediately begin attacking your gum tissues, reducing blood circulation and compromising your body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Specifically, smoking causes:
- Reduced oxygen supply to gum tissues
- Suppression of immune system responses
- Decreased production of saliva
- Accelerated bacterial growth
Progressive Oral Health Deterioration
Smoking triggers a cascading series of oral health problems. The initial damage starts with inflammation and gradually progresses toward more severe conditions. Smokers experience higher rates of tooth decay, gum disease, and oral cancer compared to non-smokers. Read more about smoking’s comprehensive dental impact with our detailed guide.
The physiological changes induced by smoking create an environment where harmful bacteria thrive.
Reduced saliva production means less natural cleaning and neutralization of acids in the mouth, further accelerating tooth decay and potential infections.
Long-Term Systemic Consequences
Beyond immediate oral damage, smoking creates long-term systemic risks. Chronic smokers are significantly more likely to develop periodontitis, a severe gum infection that can lead to tooth loss and potentially contribute to broader health complications like cardiovascular disease. The continuous exposure to tobacco’s toxic compounds progressively weakens the body’s natural defensive mechanisms, making dental recovery increasingly challenging.
The following table compares how smoking affects key aspects of oral health, summarizing the different mechanisms and their consequences as discussed in this section.
| Aspect of Oral Health | How Smoking Causes Damage | Long-Term Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Circulation | Nicotine constricts blood vessels, limiting oxygen and nutrient delivery | Impaired healing, increased gum disease risk |
| Immune Response | Tobacco suppresses white blood cells and immune defense | Higher infection rates, slower recovery |
| Oral Microbiome | Alters bacterial balance, favors harmful microbes | Increased decay, chronic inflammation |
| Tissue Structure | Chronic exposure leads to collagen loss, tissue breakdown | Permanent gum recession, bone loss |
| Cellular Health | Tobacco chemicals induce DNA mutations | Elevated oral cancer risk |
Why does smoking significantly affect dental health?
Smoking creates a devastating environment for oral health by systematically undermining the body’s natural protective mechanisms. Research from the National Institutes of Health demonstrates how tobacco fundamentally disrupts critical biological processes that maintain dental wellness.
Compromising Blood Circulation and Immune Response
Tobacco consumption dramatically reduces blood circulation in oral tissues, creating a cascade of destructive consequences. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, which significantly diminishes oxygen and nutrient supply to gum tissues. This restricted circulation impairs the body’s ability to fight infections and repair damaged tissues.
The specific mechanisms of damage include:
- Suppressing white blood cell functionality
- Reducing healing capacity of gum tissues
- Blocking essential nutrient transportation
- Preventing natural inflammatory responses
Chemical Disruption of Oral Microbiome
Smoking introduces complex chemical compounds that fundamentally alter the oral microbiome. These toxic substances create an environment where harmful bacteria thrive while beneficial bacterial populations decline. Learn more about dental microbiome impacts in our comprehensive dental health guide.
The bacterial imbalance triggered by smoking accelerates tooth decay, increases plaque formation, and creates conditions conducive to chronic oral infections. Smokers experience significantly higher rates of oral bacterial colonization compared to non-smokers.
Long-Term Structural and Genetic Damage
Beyond immediate tissue damage, smoking causes profound genetic and structural changes in oral cells. Tobacco compounds trigger mutations that can potentially lead to precancerous and cancerous transformations. Chronic smokers experience accelerated cellular aging, reduced collagen production, and compromised tissue regeneration capabilities, making dental recovery increasingly difficult and complex.
How does smoking contribute to oral diseases?
Smoking acts as a potent catalyst for numerous oral diseases, transforming the mouth into a hostile environment prone to chronic health complications. Research from the National Institutes of Health reveals the intricate ways tobacco fundamentally disrupts oral ecosystem balance.
Pathogenic Bacterial Proliferation
Tobacco consumption creates an ideal breeding ground for harmful oral bacteria. The chemical composition of cigarette smoke alters the mouth’s natural microbiological landscape, enabling aggressive bacterial strains to dominate and overwhelm protective microorganisms. This microbial shift dramatically increases risks of serious dental infections and inflammatory conditions.
Key mechanisms of bacterial transformation include:
- Reducing protective bacterial diversity
- Enhancing pathogenic bacterial growth rates
- Weakening natural immune defense mechanisms
- Creating anaerobic environments favorable to harmful microbes
Inflammatory Response Disruption
Smoking systematically compromises the body’s natural inflammatory responses, which are critical for defending against oral infections. Chronic tobacco use suppresses immune cell functionality, preventing effective healing and creating prolonged vulnerability to periodontal diseases. Discover more about dental health protection strategies in our comprehensive guide.
The persistent inflammation triggered by smoking leads to progressive tissue damage, accelerating gum recession, bone loss, and potential tooth detachment. Smokers experience significantly higher rates of chronic periodontal inflammation compared to non-smokers.
Cellular Mutation and Disease Progression
Beyond immediate bacterial and inflammatory impacts, smoking induces profound cellular mutations that predispose individuals to severe oral diseases. Tobacco compounds directly damage cellular DNA, increasing risks of precancerous transformations and malignant developments. Chronic smokers face exponentially higher probabilities of developing oral cancer, with tobacco use being a primary contributing factor to these life-threatening conditions.
What are the long-term effects of smoking on teeth and gums?
Smoking creates a devastating trajectory of progressive dental deterioration that extends far beyond surface-level damage. Research from the American Dental Association highlights the comprehensive and irreversible impacts of long-term tobacco consumption on oral structures.
Permanent Structural Degradation
Chronic smoking initiates a systematic breakdown of dental and gum tissues, causing permanent structural changes. The continuous exposure to toxic compounds leads to accelerated bone density loss in the jaw, compromising the foundational support for teeth. This progressive deterioration weakens tooth roots, increases mobility, and ultimately accelerates tooth loss.
![]()
Key structural damages include:
- Permanent reduction in bone mineral density
- Irreversible gum tissue recession
- Compromised tooth root stability
- Accelerated enamel erosion
Aesthetic and Functional Transformations
Beyond structural damage, smoking dramatically alters the aesthetic and functional characteristics of oral tissues. Persistent tobacco use causes significant discoloration, creating permanent stains that penetrate tooth enamel. Learn more about comprehensive dental restoration techniques to understand potential interventions.
Smokers experience profound changes in oral functionality, including reduced saliva production, increased sensitivity, and compromised taste perception. These functional alterations create a cascading effect that further deteriorates overall oral health and quality of life.
Chronic Disease and Cancer Risks
The most severe long-term consequence of smoking involves exponentially increased risks of oral cancer and chronic inflammatory diseases. Tobacco use fundamentally transforms cellular structures, creating environments conducive to precancerous and cancerous mutations. Chronic smokers face significantly higher probabilities of developing oral squamous cell carcinoma, with tobacco being a primary causative factor in these life-threatening conditions.
What steps can be taken to mitigate smoking’s impact on oral health?
Research from the Mouth Healthy Organization emphasizes that proactive dental care and lifestyle modifications can significantly counteract the destructive effects of tobacco consumption on oral health. Understanding strategic interventions becomes crucial for individuals seeking to protect their dental wellness.
Comprehensive Professional Dental Interventions
Professional dental care represents the most critical strategy for mitigating smoking-related oral damage. Regular dental examinations enable early detection and targeted treatment of potential complications. Dentists can provide specialized cleaning techniques, comprehensive oral assessments, and personalized treatment plans designed to address tobacco-induced structural changes.
Key professional intervention strategies include:
- Specialized deep cleaning procedures
- Advanced periodontal treatments
- Comprehensive oral cancer screenings
- Targeted rehabilitation of damaged oral tissues
Aggressive Personal Oral Hygiene Protocols
Individuals must adopt rigorous personal oral hygiene practices to counteract tobacco’s damaging effects. This involves implementing advanced cleaning techniques and using specialized dental products designed to address smoking-related challenges. Explore our detailed guide on maintaining optimal dental health to understand comprehensive prevention strategies.
Enhanced personal hygiene protocols should include using antiseptic mouthwashes, investing in high-quality electric toothbrushes, and employing specialized toothpastes formulated for smokers.
 Frequent interdental cleaning and consistent oral irrigation can help manage bacterial growth and reduce inflammatory responses.
Frequent interdental cleaning and consistent oral irrigation can help manage bacterial growth and reduce inflammatory responses.
Lifestyle Modification and Smoking Cessation
Ultimately, the most effective strategy for mitigating oral health damage involves comprehensive smoking cessation. Quitting tobacco consumption allows natural healing processes to regenerate damaged oral tissues. Individuals can seek professional support through nicotine replacement therapies, counseling programs, and medical interventions designed to facilitate successful tobacco cessation.
Reclaim Your Oral Health After Smoking
Are you struggling with the effects of smoking on your gums and teeth? The truth is, tobacco use can lead to gum disease, tooth loss, staining, and even oral cancer. This article underscores the risks of reduced gum circulation, bacterial buildup, and long-term complications that make your smile feel less healthy and your oral comfort incomplete. If you recognize yourself in these descriptions, you are not alone—many people in Edmonton experience the challenges that come with smoking’s impact on oral health.
This table summarizes professional and personal strategies to mitigate smoking’s oral health impact, highlighting how each step helps reduce risks and promote healing.
| Mitigation Step | Description | Benefit to Oral Health |
|---|---|---|
| Professional Dental Cleanings | Specialized deep cleaning and periodontal treatments | Removes buildup, slows gum disease |
| Oral Cancer Screenings | Regular assessments for precancerous or cancerous changes | Early detection of serious conditions |
| Aggressive Home Oral Hygiene | Enhanced brushing, flossing, antiseptic rinses, smoker-focused products | Reduces bacteria, manages inflammation |
| Dental Product Use | Whitening toothpaste, fluoride, high-quality brushes | Limits staining, strengthens enamel |
| Smoking Cessation Programs | Counseling, nicotine replacement, medical interventions | Enables tissue healing, lowers all risks |
| Consistent Dental Check-Ups | Frequent exams and monitoring | Detects problems early, guides solutions |

Unity Square Dental is ready to help you build a healthier future for your mouth. Our caring team uses advanced dental technology and proven periodontal therapies to address signs of gum damage, prevent further deterioration, and restore your dental confidence. We offer professional cleanings for smokers, comprehensive oral cancer screenings, and friendly advice for your unique situation. Book your personalized appointment at Unity Square Dental to take the first step. Visit our understanding gum health page to see how expert care can repair the harm and protect your smile. Your healthier smile starts with a conversation—reach out now and let us support your goal for lasting dental wellness.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does smoking affect my gums and risk of gum disease?
Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease by reducing blood circulation and impairing your immune response. To protect your gums, prioritize regular dental check-ups and commit to daily flossing and brushing to help combat these effects.
What are the visible signs that smoking is harming my oral health?
Common signs that smoking is affecting your oral health include persistent bad breath, gum recession, and stained teeth. Monitor these symptoms closely, and consult with your dentist if you notice any changes to maintain your dental wellness.
How can I improve my oral health after quitting smoking?
After quitting smoking, your oral health can improve significantly. Focus on enhancing your oral hygiene routine, including using fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash daily, which can restore balance to your oral microbiome within a few months.
What steps should I take if I notice tooth sensitivity after smoking?
Tooth sensitivity after smoking may indicate underlying damage, such as enamel erosion or gum recession. Schedule an appointment with your dentist to evaluate the issue and receive tailored interventions, which may include fluoride treatments or protective coatings to reduce sensitivity.
How long does it take for my oral health to improve after I stop smoking?
Your oral health can start to improve within 30 days of quitting smoking, as gum healing and reduction of inflammation begin. Commit to regular dental visits and a consistent oral hygiene routine to maximize these benefits over time.
What can I do to reduce the staining of my teeth from smoking?
To reduce tooth staining from smoking, consider professional teeth whitening treatments and maintain a strict oral care routine at home. Brush twice a day and use whitening toothpaste to gradually lessen discoloration and restore your smile’s brightness.
Recommended
- Understanding the Smoking Effects on Gums – Unity Square Dental
- Stress and Dental Health: Essential Guide for Edmonton Families 2025 – Unity Square Dental
- Understanding Medications That Affect Teeth Health – Unity Square Dental
- Best Foods for Oral Health: Understanding Their Impact – Unity Square Dental