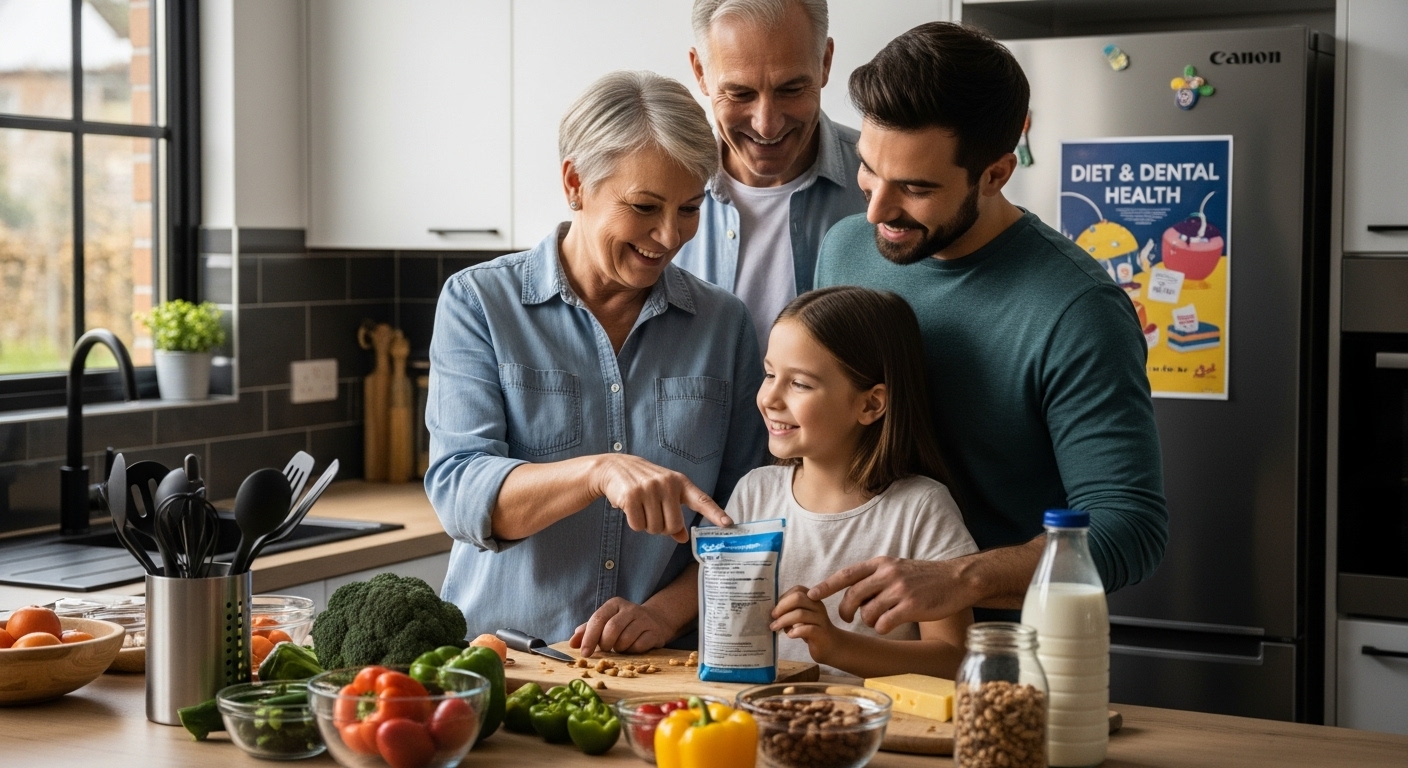
What you eat does more than just fill your stomach. Nearly 3.5 billion people worldwide suffer from oral diseases linked to poor nutrition. That sounds huge, right? Most people focus on brushing and flossing but forget that what goes into your mouth can shape the future of your teeth and gums. The real secret weapon behind healthy smiles is not in your bathroom cabinet but right on your plate.
Table of Contents
- The Role Of Nutrition In Oral Health
- Common Dietary Factors Affecting Teeth And Gums
- How Sugar Impacts Dental Health
- The Importance Of Vitamins And Minerals For Teeth
- Dietary Recommendations For Optimal Dental Care
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Nutrition directly impacts oral health. | The food you eat affects tooth strength, gum health, and overall dental integrity. |
| Limit sugar to prevent dental damage. | Sugars interact with bacteria to produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. |
| Incorporate calcium and vitamins for strong teeth. | Calcium and vitamins like D and C help maintain tooth structure and healthy gums. |
| Choose whole foods for better dental wellness. | Whole foods with high nutritional value support oral health and strengthen the immune response against bacteria. |
| Strategic meal timing minimizes oral acid exposure. | Regular meal schedules reduce the frequency of acid attacks from sugary snacks, protecting teeth from decay. |
The Role of Nutrition in Oral Health
Nutrition plays a critical role in maintaining optimal oral health, serving as a fundamental foundation for strong teeth and healthy gums. What you consume directly impacts your mouth’s ecosystem, influencing everything from tooth enamel strength to bacterial balance. Our guide on the best foods for oral health provides deeper insights into nutritional strategies.
Understanding Nutritional Impact on Dental Wellness
The human mouth is a complex environment where diet acts as a primary determinant of oral health. Nutrients interact with teeth and gums in sophisticated ways, either supporting or potentially compromising dental integrity. According to research from the National Institutes of Health, specific dietary components can significantly influence oral microbiome composition and overall dental resilience.
Key nutritional factors affecting oral health include:
- Calcium and vitamin D for bone and tooth mineralization
- Phosphorus for enamel repair and strengthening
- Vitamin C for gum tissue health and collagen production
Balancing Nutrients for Optimal Dental Protection
Balancing your diet requires understanding how different nutrients interact with your oral environment. Proteins help repair tissue, while antioxidants combat inflammation. Minerals like zinc and magnesium support immune responses within the mouth, reducing vulnerability to bacterial infections.
Professional dental nutritionists emphasize that a holistic approach to diet goes beyond simply avoiding sugary foods. Strategic nutrient intake can actively protect and regenerate oral tissues, creating a proactive defense against potential dental issues. This means consuming a diverse range of whole foods that provide comprehensive nutritional support for your teeth and gums.
Common Dietary Factors Affecting Teeth and Gums
Diet represents a profound and complex factor in maintaining oral health, with certain foods and beverages capable of either protecting or damaging dental structures. Understanding these dietary interactions helps individuals make informed nutritional choices that support long term dental wellness. Our guide on medications that affect teeth provides complementary information about additional factors impacting oral health.
Sugar and Acid: The Primary Dental Disruptors
Sugar consumption remains the most significant dietary threat to dental health.
VIDEO:video_content] When sugar interacts with oral bacteria, it produces acid that progressively erodes tooth enamel, creating an environment conducive to cavities and decay. According to [research from the Journal of Dental Research, prolonged sugar exposure dramatically increases the risk of dental caries.
Key problematic dietary elements include:
- Sugary beverages like soda and energy drinks
- Processed snacks with high refined sugar content
- Sticky candies that adhere to tooth surfaces
- Carbohydrate-rich foods that break down into simple sugars
Nutritional Protective Strategies
Balanced nutrition acts as a powerful defense mechanism against dental deterioration. Certain foods contain minerals and compounds that actively support tooth remineralization and strengthen gum tissues. Consuming foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins helps counteract potential damage from acidic and sugary dietary components.
Protective nutritional strategies involve selecting whole foods that promote oral microbiome health. Crunchy vegetables like carrots and celery mechanically clean teeth, while foods containing probiotics support beneficial bacterial populations. By strategically incorporating nutrient dense foods, individuals can create a nutritional shield that promotes comprehensive dental wellness.
How Sugar Impacts Dental Health
Sugar represents a complex and dangerous substance for oral health, acting as a primary catalyst for numerous dental problems. Its interaction with oral bacteria creates a destructive chain reaction that can compromise tooth integrity and gum wellness. Learn more about stress and dental health to understand how additional lifestyle factors contribute to oral challenges.
The Biological Mechanism of Sugar Damage
When sugar enters the mouth, oral bacteria immediately begin metabolizing these simple carbohydrates, producing acidic byproducts that erode tooth enamel. According to research from the World Health Organization, this process initiates demineralization, gradually weakening dental structures and creating vulnerability to decay.
Key stages of sugar’s destructive process include:
- Immediate bacterial consumption of sugar molecules
- Production of harmful acid as metabolic waste
- Gradual erosion of protective tooth enamel
- Creation of environment conducive to bacterial growth
Long Term Consequences of Sugar Consumption
Persistent high sugar intake transforms temporary dental damage into chronic oral health challenges.
 Repeated acid attacks progressively breakdown tooth minerals, leading to cavities, sensitivity, and potential structural compromises. The frequency of sugar consumption matters as much as total quantity consuming sugar multiple times daily creates more consistent acid environments than single large sugar exposures.
Repeated acid attacks progressively breakdown tooth minerals, leading to cavities, sensitivity, and potential structural compromises. The frequency of sugar consumption matters as much as total quantity consuming sugar multiple times daily creates more consistent acid environments than single large sugar exposures.
Dental professionals emphasize that understanding sugar’s impact goes beyond simple avoidance. Strategic management involves monitoring not just obvious sugary foods, but hidden sources like processed carbohydrates, fruits, and seemingly healthy snacks that rapidly convert to simple sugars during digestion.
The Importance of Vitamins and Minerals for Teeth
Vitamins and minerals function as essential building blocks for maintaining robust dental health, playing a critical role in tooth structure, gum protection, and overall oral resilience. Understanding their specific contributions helps individuals make informed nutritional choices that support long term dental wellness. Check out our teeth friendly snacks guide for practical dietary recommendations.
Mineral Foundation for Dental Strength
Calcium and phosphorus represent the primary mineral components responsible for tooth structure and remineralization. These minerals work synergistically to rebuild and maintain tooth enamel, creating a strong defensive barrier against bacterial invasion and decay. According to research from the National Institutes of Health, consistent mineral intake directly correlates with enhanced dental durability.
Key minerals essential for dental health include:
- Calcium for bone and tooth density
- Phosphorus for enamel repair and regeneration
- Magnesium for overall mineral metabolism
- Zinc for immune response and healing
Vitamins: The Protective Dental Allies
Vitamins serve as crucial protective agents in maintaining oral health, supporting everything from gum tissue integrity to immune system functionality. Vitamin D facilitates calcium absorption, while Vitamin C promotes collagen production critical for gum health. These micronutrients work beyond simple nutritional support, actively defending against inflammation and supporting the body’s natural healing mechanisms.
Nutritional experts emphasize that a holistic approach to vitamin intake involves consuming a diverse range of whole foods.
Below is a comparison table detailing the key vitamins and minerals discussed in the article and their roles in supporting dental health.
| Nutrient | Role in Dental Health | Example Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Builds tooth and bone density; supports enamel strength | Dairy, leafy greens, almonds |
| Phosphorus | Repairs and regenerates tooth enamel | Dairy, fish, lean meats |
| Magnesium | Supports mineral metabolism, aiding enamel formation | Nuts, seeds, whole grains |
| Zinc | Promotes immune response and healing in oral tissues | Meat, legumes, seeds |
| Vitamin D | Facilitates calcium absorption for strong teeth and bones | Eggs, fatty fish, sunlight |
| Vitamin C | Promotes gum health, collagen production, and tissue repair | Citrus fruits, peppers |
| By strategically incorporating vitamin rich ingredients, individuals can create a comprehensive nutritional shield that supports not just dental health, but overall physiological wellness. |
Dietary Recommendations for Optimal Dental Care
Making strategic dietary choices represents a powerful approach to maintaining long term dental health. Beyond simply avoiding harmful foods, individuals can proactively support their oral wellness through mindful nutrition. Explore our guide on healthy snacks for teeth to discover practical dietary strategies.
Foods That Promote Dental Health
Certain foods act as natural defenders of oral wellness, providing mechanical cleaning and nutritional support. Crunchy vegetables like carrots and celery stimulate saliva production, which helps neutralize acids and wash away harmful bacteria. According to research from the Journal of Dental Research, consuming foods rich in fiber and nutrients can significantly reduce the risk of dental decay.
Key foods that support dental health include:
- Dairy products with calcium and phosphorus
- Leafy green vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Nuts and seeds
- Water rich fruits and vegetables
Strategic Dietary Considerations
Effective dental nutrition extends beyond individual food choices to encompass broader eating patterns. Frequency of consumption matters as much as the specific foods consumed. Continuous snacking or sipping sugary beverages creates prolonged acid environments in the mouth, increasing dental vulnerability. Dental nutritionists recommend structured meal times and minimizing between meal consumption of acidic or sugary items.
Professional recommendations emphasize developing a holistic approach to nutrition that balances oral health needs with overall dietary wellness.
 This means creating meal plans that not only protect teeth but also support comprehensive nutritional requirements.
This means creating meal plans that not only protect teeth but also support comprehensive nutritional requirements.
Ready to Take Control of Your Dental Wellness Through Better Nutrition?
Are you concerned about how your diet may be affecting your teeth and gums? The article explained how everyday choices like sugar intake and vitamin deficiencies can have a lasting impact on your smile. You might be feeling overwhelmed by mixed advice or worried that your eating habits are causing hidden dental problems. Every meal influences your oral health but you do not have to face these challenges alone.

Unity Square Dental is here to support your journey to a healthier mouth. Our experienced team offers personalized guidance and advanced care to make sure your nutrition and dental health work together for the best results. Take the next step by booking an appointment through our easy online booking page where you will find information about our welcoming clinic. You can also visit our teeth friendly snacks guide for simple daily changes that improve your dental wellness. Start with us today and see how small nutrition shifts combined with expert dental care can make a lasting difference in your life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What nutrients are essential for maintaining good dental health?
Calcium, phosphorus, and vitamins such as vitamin D and vitamin C are essential for maintaining good dental health. These nutrients contribute to tooth structure, gum tissue integrity, and overall oral resilience.
How does sugar consumption affect tooth enamel?
Sugar consumption leads to the production of acid by oral bacteria, which erodes tooth enamel. The longer sugar interacts with teeth, the more likely it is to create an environment conducive to cavities and decay.
What are some foods that support oral health?
Foods that support oral health include dairy products rich in calcium, leafy green vegetables, crunchy fruits and vegetables like carrots and celery, lean proteins, and nuts and seeds. These foods provide essential nutrients and help mechanically clean teeth.
How can I balance my diet to protect my dental health?
Balancing your diet involves consuming a variety of whole foods that are rich in essential nutrients while minimizing intake of sugary and acidic foods. Establish structured meal times and avoid frequent snacking on harmful foods to protect your dental health.
Recommended
- Stress and Dental Health: Essential Guide for Edmonton Families 2025 – Unity Square Dental
- Best Foods for Oral Health: Understanding Their Impact – Unity Square Dental
- 10 Teeth Friendly Snacks for Healthy Smiles – Unity Square Dental
- Understanding Medications That Affect Teeth Health – Unity Square Dental